Economic growth and development are central pillars of a nation’s economic well-being and progress. These concepts encompass the quantitative and qualitative improvements in an economy’s output, income distribution, and living standards. This comprehensive guide delves into economic growth and development, explores relevant theories, discusses Indian perspectives, and illustrates key concepts with examples.
Understanding Economic Growth & Development
- Economic Growth: Refers to the sustained increase in a country’s real GDP (Gross Domestic Product) over time. It signifies the expansion of an economy’s capacity to produce goods and services.
- Economic Development: Encompasses a broader range of improvements, including income distribution, healthcare, education, and overall well-being. It reflects not only higher income levels but also a better quality of life.
Theories of Economic Growth
- Solow Growth Model: Developed by Robert Solow, this model suggests that economic growth depends on factors such as capital accumulation, technological progress, and labor force growth.
- Endogenous Growth Theory: Proposes that technological progress is not an exogenous factor but can be influenced by policies and investments in human capital and research and development.
- Harrod-Domar Model: Focuses on the role of investment in generating economic growth. It suggests that an increase in investment can lead to an expansion of output and employment.
- Lewis Model: Introduced by Arthur Lewis, this model explores the transition from a dualistic economy (with a surplus agricultural sector) to a more modern industrialized economy.
Economic Growth vs. Economic Development
- Economic growth primarily concerns quantitative expansion, measured by GDP growth rates.
- Economic development encompasses qualitative improvements, including better living standards, poverty reduction, and access to basic services.
Indian Perspectives on Economic Growth & Development
- Five-Year Plans: India’s economic development is guided by Five-Year Plans, outlining goals, priorities, and policies for balanced growth.
- Poverty Alleviation Programs: Initiatives like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) aim to reduce poverty and promote economic development.
- Human Development Index (HDI): India evaluates development using the HDI, which considers factors like life expectancy, education, and income.
Examples of Economic Growth & Development
- India’s Green Revolution: The adoption of high-yielding crop varieties and modern agricultural practices significantly increased agricultural output, contributing to both economic growth and rural development.
- China’s Economic Transformation: China’s rapid economic growth lifted hundreds of millions out of poverty, but development challenges include income inequality and environmental degradation.
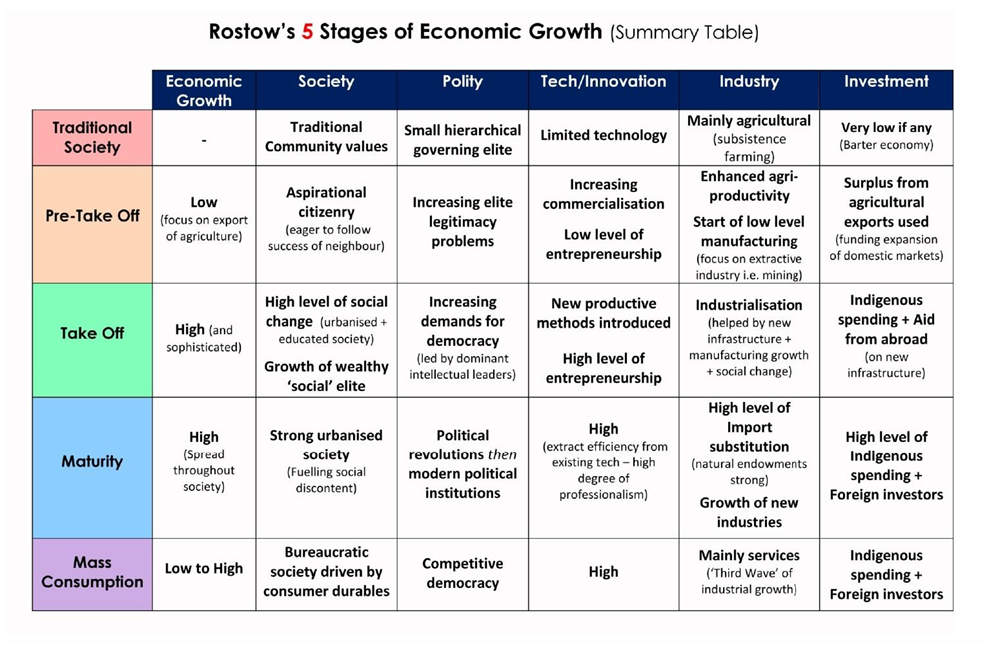
Factors Influencing Economic Growth & Development
- Investment in Human Capital: Education and skill development contribute to a skilled workforce, fostering economic development.
- Infrastructure Development: Access to transportation, energy, and communication networks facilitates economic growth.
- Innovation and Technology: Technological advancements drive economic growth by increasing productivity.
- Institutional Framework: Sound institutions and good governance create an enabling environment for development.
- Income Distribution: Equitable income distribution fosters social cohesion and development.
- Global Trade: Engaging in international trade can stimulate economic growth by expanding markets.
Challenges in Economic Development
- Income Inequality: Disparities in income and wealth can hinder overall development and social cohesion.
- Environmental Sustainability: Unsustainable practices can lead to ecological degradation and jeopardize long-term development.
- Access to Education and Healthcare: Unequal access to these essential services can hinder human development.
- Corruption: Corruption undermines the effectiveness of policies and investments intended for development.
- Political Instability: Political unrest and instability can disrupt development efforts.
Measuring Economic Development
- GDP per capita: A common metric that divides a country’s GDP by its population, providing an average income per person.
- Human Development Index (HDI): A composite index that combines indicators of life expectancy, education, and income.
- Gini Coefficient: Measures income inequality, with a lower score indicating more equitable income distribution.
- Poverty Headcount Ratio: The percentage of the population living below the poverty line.
Historical Context
- Post-World War II: The post-war period witnessed rapid reconstruction and economic growth in Western nations.
- Decolonization: Newly independent nations in Africa and Asia faced the challenges of development.
- Globalization: The interconnectedness of economies in the late 20th century influenced development strategies.
Success Stories in Economic Development
- Singapore: Rapid industrialization, investments in education, and a strong institutional framework transformed Singapore into a high-income nation.
- Norway: Prudent resource management and a strong welfare state contribute to Norway’s high HDI ranking.
- Costa Rica: Costa Rica’s investment in education, healthcare, and environmental conservation has led to a relatively high standard of living in Latin America.
Global Initiatives for Development
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): These 17 goals aim to address various aspects of development, including poverty, health, education, and environmental sustainability.
- International Aid and Assistance: Developed nations provide aid to less developed countries to support their development efforts.
- International Trade Agreements: Bilateral and multilateral trade agreements aim to stimulate economic growth through increased trade.
Urbanization and Economic Development
- Urbanization often accompanies economic development as people migrate from rural areas to cities in search of better opportunities.
- Challenges: Urbanization can strain infrastructure and lead to issues like slums and congestion.
Key Takeaways
- Economic growth represents quantitative expansion, while economic development encompasses qualitative improvements in living standards and well-being.
- Theories of economic growth include the Solow Model, Endogenous Growth Theory, and more.
- India pursues development through Five-Year Plans, poverty alleviation programs, and the Human Development Index.
- Challenges in development include income inequality, environmental sustainability, and access to essential services.
- Measuring development involves various metrics, including GDP per capita, HDI, Gini Coefficient, and poverty headcount ratio.
Economic growth and development are complex, multifaceted processes that vary across countries and regions. Understanding these concepts and their underlying theories is essential for policymakers, economists, and citizens striving to improve the economic well-being of their communities and nations.
4 responses to “Chapter 3 – Economic Growth & Development: Impact, Factors and Challenges.”
-
I have read some excellent stuff here Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting I wonder how much effort you put to make the sort of excellent informative website
-
I do believe all the ideas youve presented for your post They are really convincing and will certainly work Nonetheless the posts are too short for novices May just you please lengthen them a little from subsequent time Thanks for the post
-
Thanks I have just been looking for information about this subject for a long time and yours is the best Ive discovered till now However what in regards to the bottom line Are you certain in regards to the supply
-
Your blog is a testament to your dedication to your craft. Your commitment to excellence is evident in every aspect of your writing. Thank you for being such a positive influence in the online community.



Leave a Reply