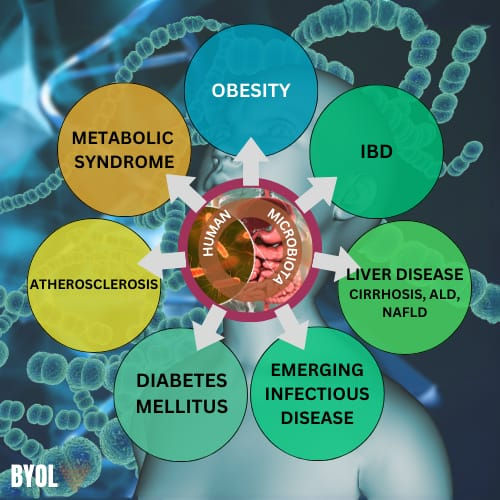
The human microbiota, along with over 100 trillion microorganisms, plays a vital function in fitness and disease. The gut microbiota, regularly considered an "Crucial Organ," carries around 150 times greater genes than the Human Genome. It is worried in key biological techniques along with metabolism, epithelial development, and immune law. When balance of microbiota is disrupted , it can leads to variety of long- term problem includes chronic sicknesses, consisting of weight problems, Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, Atherosclerosis, Alcoholic liver Ailment (ALD), Non-alcoholic Fatty liver Ailment (NAFLD), Cirrhosis, and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Microbiota: “A key Player in Health and Disease”.
The Human Microbiota, a diverse community of microorganisms residing in the gut, mouth, skin, and respiratory tract, plays a pivotal role in maintaining homeostasis and immune regulation. When this microbial balance is disturbed, a condition known as Dysbiosis, it can impair vital physiological functions, contributing to the onset of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and respiratory disorders. This review explores the microbiota's impact on key health pathways, including the Gut-Brain Axis, immune system modulation, and disease progression through Microbial Imbalances, Immune Dysregulation, and Chronic Inflammation. Additionally, we examine clinical approaches like microbiota modulation and fecal microbiota transplantation, which hold promise for restoring balance and treating various health conditions.
As science continues to uncover the profound influence of microbiota, it becomes clear that nurturing these tiny organisms is key to a healthier future. Let’s explore their fascinating role in both health and disease.
Microbiota and its Composition
The human body host a diverse range of microbiota, a unique collection of microorganisms that support health across different areas, including –
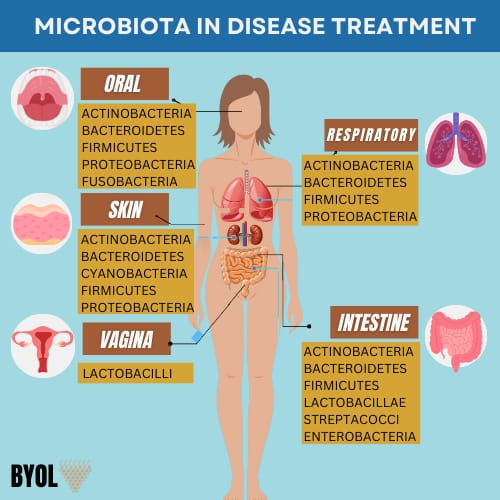
Gut Microbiota: The most notable and observed, nurturing over 100 billion bacteria, most of them found in intestines, where they aid digestion and overall health.
Skin Microbiota: Our body’s first line of defense, working endlessly to prevent infection and keep our skin healthy and resilient.
Oral Microbiota: The guardians of mouth, Promotes oral hygiene and prevent dental disease.
Respiratory Microbiota: Silent protector of Lungs, it boost immunity and protects from respiratory infections.
Urogenital Microbiota: Key to maintaining the fragile microbial harmony in the urinary and reproductive system.
Each person's microbiota is unique as a fingerprint. It determined by factors such as genetics, diet, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
The Role of Microbiota in Promoting Health :
A healthy microbiota is crucial for contributing many physiological functions, such as:
Digestion and Nutrition Support –
Helps in break down of minerals and carbohydrates in complex foods.
Produces vital vitamins such as vitamin K and B vitamins, beneficial for overall health.
Enhances absorption of minerals such as calcium and magnesium, promoting bone and muscle health.
Protect against harmful bacteria by rivaling for nutrients and space, for maintaining healthy gut.
2. Immune Defense Regulation -
They shape and train the immune system to identify between harmful and beneficial microorganisms.
Produces antibacterial properties that work as infection prevention.
Regulates the immune response to defend against autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammation.
3. Metabolic Functions-
It contributes greatly to balancing Metabolism, guiding energy utilization and expenditure.
It produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that nourish the gut and optimize metabolism.
Influence insulin response and fat metabolism, help in weight maintenance and metabolic health.
4. Neurological and Mental Health Impact-
Communication between the microbiota and brain affects mood and cognitive function through the nervous system.
Produces neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which directly influenced mental well-being.
Plays key role in reducing anxiety, Depression and stress levels, providing a holistic approach to mental health.
5. Skin and Oral Health
Helps maintain the skin’s function and prevents diseases like acne and eczema.
Support oral health and reducing gum disease.
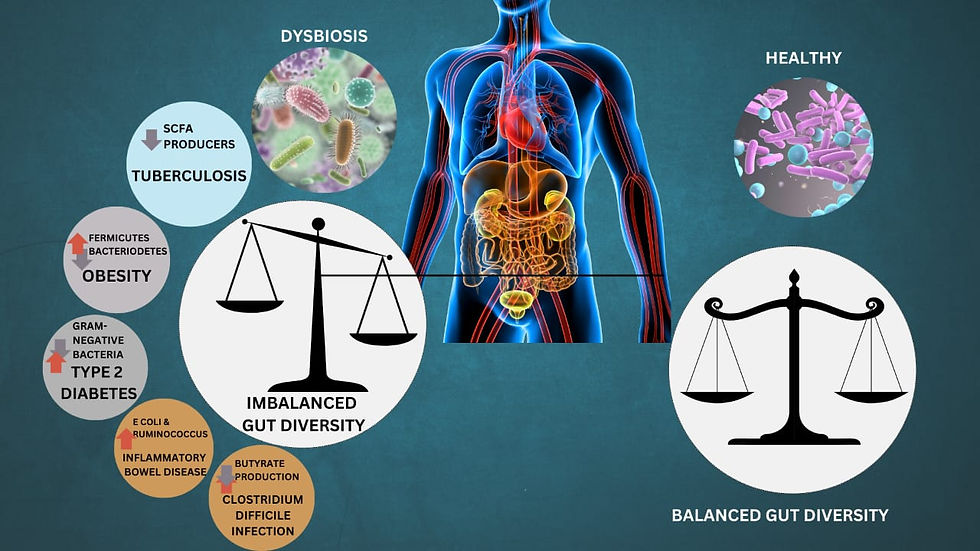
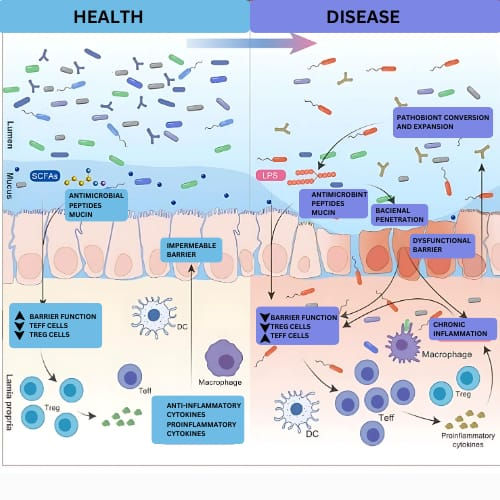
Microbes and Disease: The Consequences of Dysbiosis -
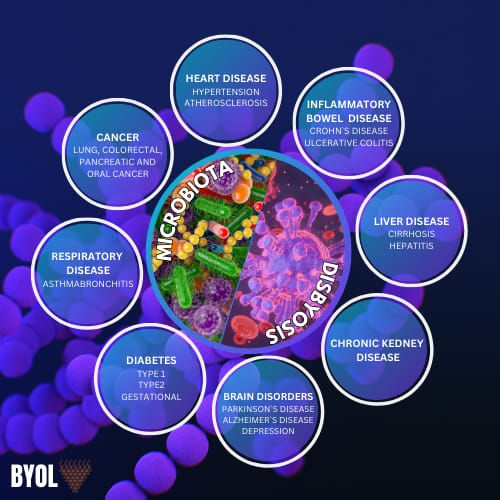
When the delicate balance of microbiota is disrupted, It can leads to various diseases such as-
Gastrointestinal Disease
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Alteration in the gut microbiota can leads to the symptoms like bloating, constipation, or diarrhea.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Condition like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, originates from the gut bacteria disruption and a compromised immune system.
Clostridium Difficile Infection (CDI): Overgrowth of harmful bacteria resulting from antibiotic use can leads to severe diarrhea and complication.
Metabolic Disorders -
Obesity: Disruption in gut bacteria, can lead to fat storage and increased energy consumption.
Type 2 Diabetes: Disruption in gut microbiota leads to insulin resistance and glucose intolerance.
Nonalcoholic Fatty liver Disease (NAFLD): Dysbiosis can cause fat accumulation and inflammation in the liver, affecting liver function.
Autoimmune Diseases-
Autoimmune Diseases: Diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are linked to damage to the intestinal lining by microbiota imbalance.
Allergies and Asthma: Overactive immune imbalance Induced microbiota disruption, leads to allergy and asthma.
Neurological and Mental Health Issues -
Depression and Anxiety: Damaged gut microbiome can lead to disrupt in lymphocyte production and cause inflammation, contribute mental health issues.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Changes in microbiota composition in children with ASD.
Parkinson's Disease: Emerging research points to a link between gut inflammation and neurological disease.
5. Cardiovascular Disease -
Certain gut bacteria produce metabolites such as trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), that associated with heart disease.
Inflammation related condition like GERD causes atherosclerosis and high blood pressure.
6. Cancer-
Chronic inflammation caused by dysbiosis may increase the risk of colon and colorectal cancer.
Disturbance in Microbiota can directly cause tumor formation by damaging DNA, inducing inflammation, and producing metabolites that promote tumor growth.
Factors Affecting Microbiota Balance-
There are many factors that influence the composition and stability of microorganisms, such as-
Diet: High-fiber, plant-based foods nourishes beneficial bacteria, while processed foods and sugar promote harmful bacteria.
Antibiotic use: Excessive use of antibiotics can disrupt the microbiota balance resulting in dysbiosis.
Hygiene: Excessive cleaning and hygiene practice can reduce microbial exposer.
Stress: Chronic stress alter the gastric secretion and weakens the intestinal barrier function.
Sleep Quality: Inadequate sleep quality impact the microbial activity and health further affecting overall well being.
Environmental Toxins: Exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and heavy metals can disrupt the microbial composition, causing potential health issues.
Strategies for Nurturing Maintaining a Healthy Microbiota-
To maintain a balanced, thriving microbiome is key to optimal health. Consider using the following steps:
Consume Microbiota – Friendly Diet
Enjoy probiotic food like yogurt, kefir, and kimchi to introduce beneficial bacteria.
Eat probiotic foods like garlic, lentils, bananas, beans , and whole grains to nourish these helpful microbes.
Include a variety of plant based foods to support a variety of bacteria.
Limit Antibiotic Use -
Take antibiotics only if needed and as directed by your health care provider.
Follow up with probiotic supplementation after antibiotic treatment.
Manage Stress Effectively-
Engage in mindfulness practices such as Meditation, Yoga, and Deep Breathing.
Prioritize relaxation to support Gut – Brain Communication.
Maintain Good Sleep Hygiene-
Try to get 7-9 hours of quality sleep every night to promote gut health.
Stay Physically Active-
Regular exercise promotes a healthy gut microbes and nervous system health.
Stay Hydrated-
Drinking plenty of water to support digestion and keeps the intestines healthy.
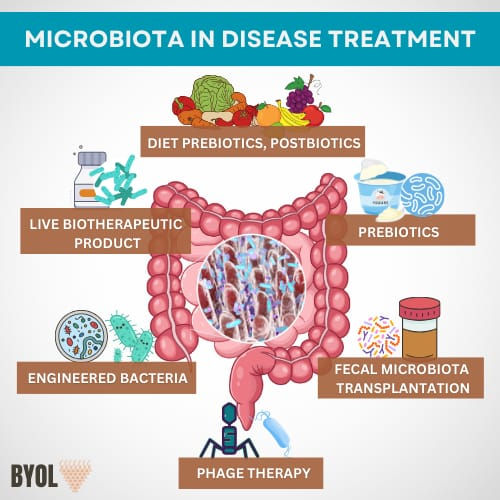
The human microbiota plays a vital role in health and disease, impacting conditions from metabolic disorders to cancer. Imbalances in gut microbiota, known as Dysbiosis, are linked to diseases like Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), Obesity, and Diabetes. Restoring balance through probiotics, prebiotics, and diet shows promise in managing these conditions.
Research also suggests the gut microbiome can influence cancer treatments, enhancing the effectiveness of Immunotherapy and Chemotherapy. Innovative therapies, such as Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT), are being explored to improve treatment outcomes. Despite challenges in fully understanding microbiota-disease interactions, ongoing research holds promise for revolutionizing disease treatment worldwide.
Future Directions in Microbiota Research-
Advances in microbiome research continues to evolve, opening new frontiers in clinical practice, including -
Personalized Nutrition: Tailor diet specifically, optimize unique microbiome for optimal health.
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT): It is promising therapeutic techniques that reintroduces healthy microbiome into the gut, especially those suffer from severe dysbiosis, offering a hope for variety of gastrointestinal issues.
Future of microbiota research is shaping the way for personalized health strategies that transform how we approach disease prevention and treatment.
Probiotics and Prebiotic Supplements:
• Probiotics are known to restore bacterial balance in the gut by preventing harmful bacteria from taking over, with research highlighting their potential to support immune function, metabolism, and gut health. However, evidence remains mixed, and probiotics may pose risks for individuals with weakened immune systems, causing infections or other complications.
• Prebiotics compiled in 2017 are formulation created from intestinal microorganisms selected to provide health benefits. The most common prebiotics include inulin, Fructo-Oligosaccharides (FOS) and Galacto-Oligosaccharides (GOS). Which grows beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacterium and lactobacillus. That helps regulate the immune system and prevents infections from multiplying. However, its clinical use is still controversial. This is because some studies have shown that prebiotics can promote tumor growth based on individual genetic differences. Butyrate, an important protein, is known to inhibit tumors and can be harmful. It depends on Genetic background, Age and Association with other pathogens.
Developing Targeted Therapies for Specific Health Conditions
Microbiome therapy:
Exploring how the microbiome may affect cancer treatment and drug efficacy.
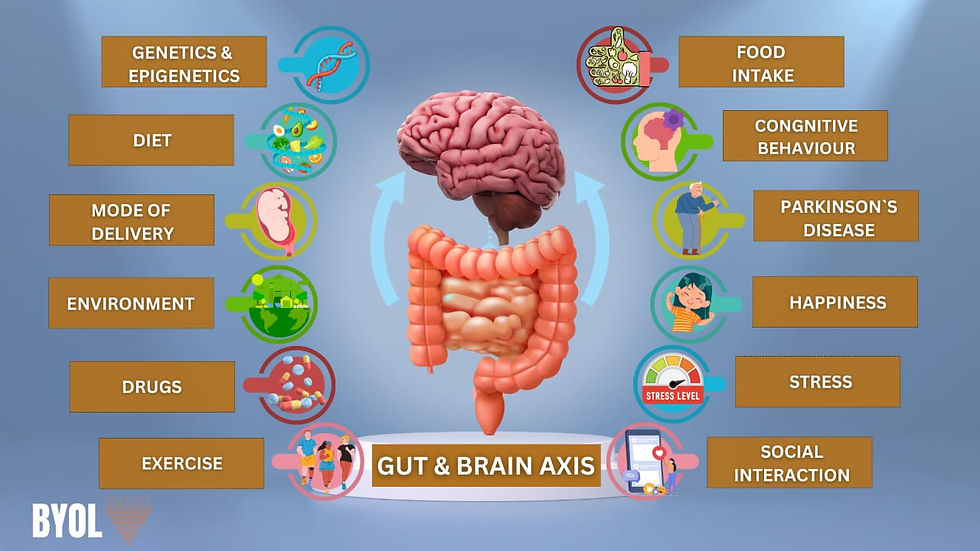
Gut-Brain Axis: The Hidden Connection-
The gut-brain axis is the powerful link between our gut and brain, where they communicate through signals like hormones and neurotransmitters. The gut, often called the "second brain," houses millions of neurons and trillions of microbes that influence our mood, stress levels, and even cognitive function. Imbalances in this system can lead to mental health issues like anxiety and depression. Understanding this connection opens new doors for treating brain-related disorders by improving gut health.
Conclusion-
The human microbiome is an important part of overall health. This affects digestion, immunity, metabolism, and even mental health. Maintaining a balanced microbiome through a healthy diet, lifestyle changes and judicious use of medication. It can lead to better disease prevention and long-term health. Because research continues to reveal the negative effects of the microbiome, Personal health products will become more available. By taking care of your microbiome .It means taking care of your health.
References -
Ursell, L. K. et al. The intestinal metabolome: an intersection between microbiota and host. Gastroenterology 146, 1470–1476 (2014).
Grice, E. A. & Segre, J. A. The human microbiome: our second genome. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 13, 151–170 (2012).
Berg, G. et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 8, 103 (2020).
Shreiner, A. B., Kao, J. Y. & Young, V. B. The gut microbiome in health and in disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 31, 69–75 (2015).
Hillman, E. T., Lu, H., Yao, T. & Nakatsu, C. H. Microbial ecology along the gastrointestinal tract. Microbes Environ. 32, 300–313 (2017).
Laterza, L. et al. The gut microbiota and immune system relationship in human graft-versus-host disease. Mediterranean J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 8, 2016025 (2016).
Auchtung, T. A. et al. Investigating colonization of the healthy adult gastrointestinal tract by fungi. mSphere. 3, e00092–18 (2018).
Lozupone, C. A. et al. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 489, 220–230 (2012).


We have understood by this article....how much microorganisms are important for our health.
Attention to almost every aspect.
Most needed and informative stuff
Good health is the foundation ofa Happy life so read this
This is eye opening stuff.
This post is incredibly informative! I especially appreciated the clear explanations and the concise summary. The content is well-researched and presented in an engaging way, making a complex topic much easier to understand. Thanks for sharing such valuable insights!