Peripheral nerves serve as the communication pathways that link the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Through […]
Growing danger of metabolic disorders

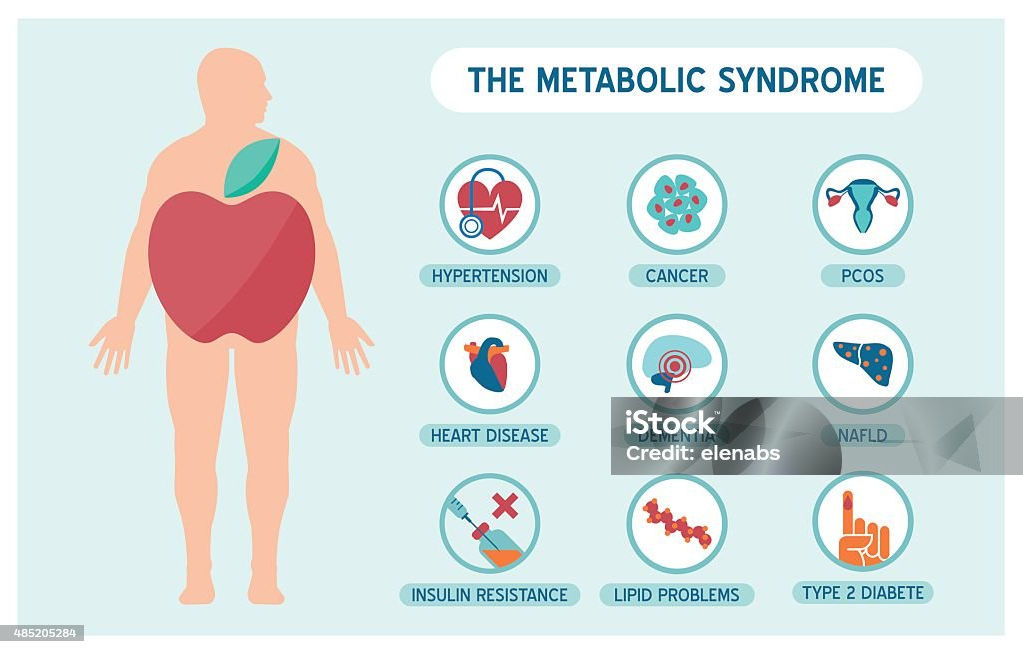
Metabolic disorders, encompassing a spectrum of conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and metabolic syndrome, are rapidly emerging as a major global health challenge. These disorders, characterized by disruptions in the body’s ability to process and utilize energy, pose significant risks to individual health and strain healthcare systems worldwide. Fueled by the modern lifestyle – characterized by sedentary habits, the overconsumption of processed foods, and chronic stress – the prevalence of these disorders is escalating at an alarming rate.
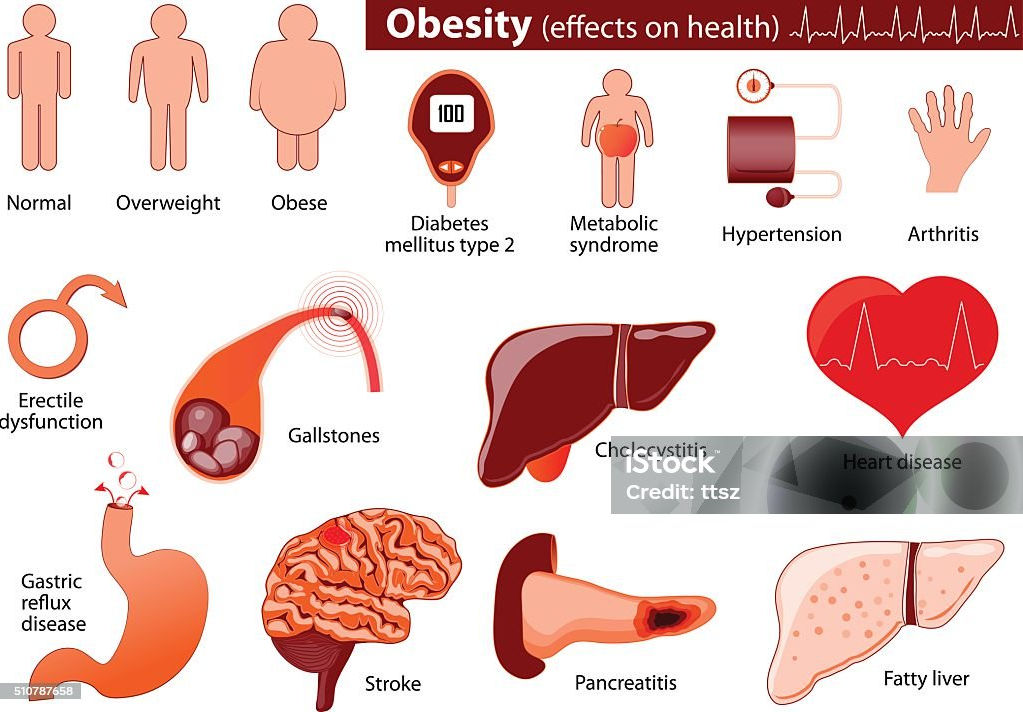
Metabolic disorders, a spectrum of conditions that impact how the body metabolizes food and utilizes energy. Obesity, characterized by excessive accumulation of body fat, is a significant driver of many metabolic disorders. Type 2 diabetes, resulting from insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production, is a major global health concern. NAFLD, a condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver, is on the rise and can progress to serious liver complications. Metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, abnormal cholesterol levels, and excess abdominal fat, significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
The global burden of metabolic disorders is staggering. Over a billion people worldwide are currently obese, with millions more affected by diabetes and NAFLD. These conditions are not merely isolated occurrences; they are intricately linked and often co-exist, creating a complex web of health challenges. The health consequences of these disorders are severe and far-reaching. Individuals with metabolic disorders face an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, liver disease, kidney failure, and even some types of cancer. Furthermore, these conditions can significantly impact mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and social isolation. The economic burden of metabolic disorders is substantial, encompassing healthcare costs, lost productivity, and reduced quality of life.
The modern lifestyle plays a significant role in the escalating prevalence of metabolic disorders. Unhealthy dietary patterns, characterized by excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats, contribute significantly to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction. Sedentary lifestyles, driven by increased screen time and reduced physical activity, further exacerbate the problem. Chronic stress, sleep disturbances, and environmental factors also play crucial roles in the development of these disorders.
Combating the growing tide of metabolic disorders requires a multi-pronged approach. This includes promoting healthy dietary patterns, emphasizing whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein; encouraging regular physical activity, including both aerobic exercise and strength training; and prioritizing stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and adequate sleep. Developing and refining medications that effectively target the underlying causes of these disorders, such as insulin resistance, obesity, and fatty liver disease, is crucial. Utilizing precision medicine approaches to tailor treatment plans based on individual genetic and metabolic profiles will also be essential. Leveraging digital health tools and artificial intelligence to monitor health data, track lifestyle behaviors, and provide personalized health guidance is another key area. Developing non-invasive diagnostic tools for early detection and monitoring of disease progression is also vital.
Furthermore, public health initiatives play a critical role. Implementing policies that promote healthy food access and affordability, such as sugar taxes and subsidies for healthy foods, is essential. Creating supportive environments that encourage physical activity, such as walkable communities and accessible parks, is crucial. Raising public awareness about the dangers of metabolic disorders and promoting healthy lifestyle choices through public health campaigns is also vital.
The journey towards addressing the global challenge of metabolic disorders will undoubtedly be complex and multifaceted. Early detection, prevention, and personalized treatment approaches are crucial to mitigating the impact of these disorders and improving the health and well-being of individuals and communities worldwide.